The E 410 food additive, also known as locust bean gum, is widely used in the food industry. This thickening agent is derived from the seeds of carob trees. Many food products, such as ice cream and sauces, contain E 410 for its ability to enhance texture. However, concerns about its safety persist.
Dr. Emily Stokes, a food safety expert, states, "While E 410 is generally recognized as safe, its effects can vary between individuals." This highlights the complexity surrounding food additives. Some may tolerate E 410 well, while others may experience adverse reactions.
The industry often emphasizes the need for rigorous testing. Yet, consumers remain curious. How much do we really know about the long-term effects of E 410? Transparency in ingredient labeling is essential. As more people become health-conscious, the demand for clear information rises. Understanding additives like E 410 is crucial for informed choices.
E 410, commonly known as carob bean gum, is a food additive derived from the carob tree's seeds. This natural thickening agent falls under the category of hydrocolloids. Hydrocolloids are substances that can form gels. E 410 is often used in dairy products, sauces, and baked goods. It helps to improve texture and stability in food products.
Research from the International Food Additives Council indicates that E 410 is generally recognized as safe when consumed within the acceptable daily intake levels. However, some studies suggest that excessive consumption can lead to gastrointestinal issues. This report highlights the importance of moderation. While E 410 can enhance food quality, its overuse may impact digestive health.
The classification of E 410 within the food additive spectrum raises some questions. Although it is plant-based, its processing can vary significantly. Not all E 410 products are created equal. Some may contain additives or contaminants due to manufacturing practices. This inconsistency may lead to consumer uncertainty. It reflects the need for transparency in food labeling. The complexity of food additives like E 410 invites reflection on how consumers can make informed choices about their diet.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Additive Name | E 410 |
| Common Name | Locust Bean Gum |
| Source | Extracted from the seeds of the carob tree |
| Classification | Thickener and stabilizer |
| Common Uses | Used in dairy, desserts, and sauces |
| Safety Assessment | Considered safe by EFSA and FDA |
| Possible Side Effects | May cause digestive issues if consumed in large amounts |
| Regulatory Status | Approved for use in food products in many countries |
E 410, also known as carob bean gum, is a food additive derived from the seeds of the carob tree. This thickening agent is commonly found in various food products. It enhances texture and stability, making it a favorite in the food industry. You'll find E 410 in items like ice creams, sauces, and salad dressings.
The versatile nature of E 410 makes it useful in a wide range of applications. It helps improve consistency in products like dairy substitutes and gluten-free items. Industry reports, such as those from the Food Additive Status Review, indicate that carob bean gum can enhance mouthfeel. This is especially important for products aimed at consumers seeking healthier options.
While E 410 is generally recognized as safe, some people may experience allergic reactions. Research suggests that reactions are rare. Furthermore, the sourcing of carob beans raises questions about sustainability and ethical practices. This uncertainty calls for more transparent supply chains and better labeling for consumers. It's crucial to monitor the impact of such additives on our diet and overall health.
E 410 is a food additive derived from carob beans. It acts as a thickening and stabilizing agent. Many people wonder about its safety for consumption. Health assessments are key to understanding potential effects.
Research shows that E 410 is generally recognized as safe. However, reactions can vary among individuals. Some may experience gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic responses. It’s crucial to monitor how your body reacts if you consume products containing E 410.
Regular assessments by health organizations help ensure its safety. Nonetheless, more studies are needed. The long-term effects are still not fully understood. Balancing enjoyment of processed foods with health awareness is important. Awareness can lead to better choices. Always read labels and listen to your body’s responses.

E 410, also known as locust bean gum, is a food additive derived from the seeds of the carob tree. It is used as a thickener and stabilizer in various food products. Regulatory bodies, including the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have established guidelines for its use. These organizations consider E 410 to be safe within specified limits. Studies show that daily intake levels are well below the maximum acceptable levels set by these authorities.
The safety assessments by EFSA indicate that E 410 poses minimal health risks. Still, there have been discussions regarding its digestive effects. While E 410 is generally recognized as safe, some individuals may experience digestive discomfort. The acceptable daily intake (ADI) is yet to be firmly established, leading to ongoing research in this area. This uncertainty calls for vigilant consumption, especially for those sensitive to certain additives.
Manufacturers are required to follow strict labeling guidelines. This ensures transparency about the ingredients used in food products. The challenges lie in ensuring that consumers are well-informed. No food ingredient is entirely without risk. Continuous monitoring and research are essential to better understand the long-term effects of E 410 on human health. These insights could help refine safety standards and improve consumer understanding.
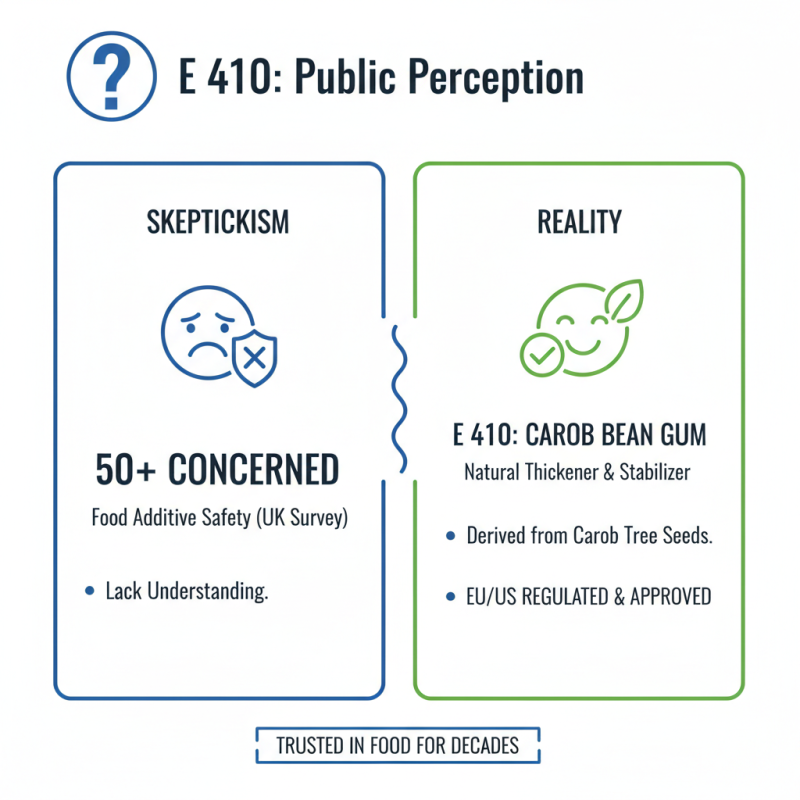
Public perception of E 410, also known as carob bean gum, varies significantly. Many consumers view food additives with skepticism. A survey by the Food Standards Agency found that over 50% of people are concerned about the safety of food additives. This confusion often stems from a lack of understanding regarding their functions and regulations.
Controversies arise when discussing the implications of E 410 on health. Some studies suggest potential allergies and digestive issues linked to synthetic additives. However, regulatory bodies like the European Food Safety Authority declare E 410 safe when used within approved limits. Contradictory data from different studies leads to mixed messages in public discourse. Many people remain unaware that JECFA, the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, has set acceptable daily intake levels for E 410. Yet, skepticism persists as consumers look for more natural ingredients.
The challenge lies in balancing safety and consumer expectations. As global food trends shift towards clean eating, additives like E 410 face backlash. Consumer interest in transparency pushes food producers to rethink ingredient lists. This raises questions about the future role of synthetic additives, despite their safety profiles. Many seek simplicity in their diets and demand clarity.






